Vitamin C What Does It Do

Last Updated on January 3, 2020 by
 Vitamin C is an essential micronutrient that plays a part in numerous vital processes in our body.
Vitamin C is an essential micronutrient that plays a part in numerous vital processes in our body.
This article will examine what vitamin C is, what it does, and the science-backed health benefits it has.
Additionally, we will look at how much vitamin C we need per day and how requirements can change.
What Is Vitamin C?
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that also goes by the name of ascorbic acid.
This vitamin plays an essential role in human health.
What Does It Do?
Firstly, vitamin C is involved in the growth and repair of tissue throughout the body (1).
Secondly, the vitamin has antioxidant properties, and it may help to protect against various disease states.
However, these are just two of the primary roles the vitamin has, and it has many other functions throughout the body.
Sources of Vitamin C
In general, vitamin C is present in most fruit and vegetables.
If you want to get more vitamin C in your diet, then bell peppers, leafy green vegetables, and yellow to red-flesh fruits are among the highest sources.
Perhaps surprisingly, organ meat (offal) is also a good source of vitamin C. Foods such as liver and beef spleen offer just as much of the vitamin as fruit do.
For a full guide to food sources, see here: the top twenty foods rich in vitamin C.
Key Point: Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is an essential water-soluble vitamin. Biologically, it has numerous important functions, and it exhibits antioxidant properties.
How Much Vitamin C Do You Need Per Day?
Firstly, no universal amount of vitamin C will be the perfect fit for everybody.
For instance, vitamin C plays a vital role in attenuating smoking-related damage.
Regarding the latter point, this means that people who smoke will benefit from a higher vitamin C requirement to protect their health (2).
That said, there are some recommended daily allowances for vitamin C that try to demonstrate the "sufficient level" of vitamin C for all people.
The table below shows these recommended values (3);
| Age/Group | Male | Female |
| 0 – 6 months | 40 mg | 40 mg |
| 7 – 12 months | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| 1 – 3 years | 15 mg | 15 mg |
| 4 – 8 years | 25 mg | 25 mg |
| 9 – 13 years | 45 mg | 45 mg |
| 14 – 18 years | 75 mg | 65 mg |
| 19 + years | 90 mg | 75 mg |
| Smokers | 125 mg | 110 mg |
| Pregnant | – | 120 mg |
| Lactating | – | 85 mg |
As shown, the daily vitamin C dosage for male adults, female adults, and children is slightly different.
However, none of these values are overly difficult to meet.
For instance, a single regular-sized yellow bell pepper provides 341 mg of vitamin C – over five times the recommended daily allowance.
Key Point: Vitamin C requirements are not universal, and they can change depending on age, gender, smoking status, and more.
Vitamin C Benefits
As part of an overall healthy diet and lifestyle, an adequate amount of vitamin C can help with many things.
We will now examine some of the ways vitamin C is good for you.
1) Influences the Growth and Repair of Body Tissues, and Helps With Wound Healing
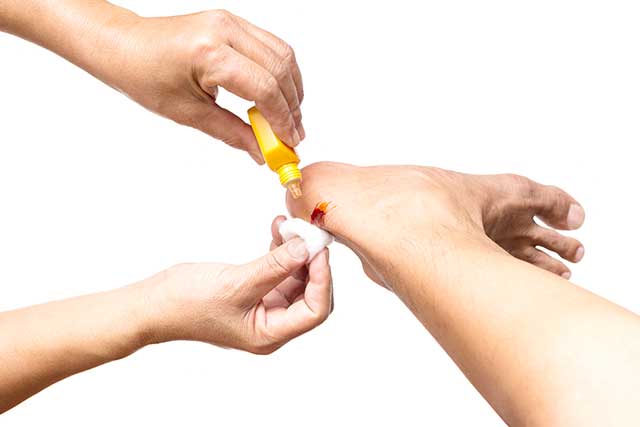
One of the most significant health benefits of vitamin C is the role it plays in the growth and repair of body tissues.
Vitamin C assists in the manufacture of proteins which help to make new skin and blood vessels.
Similar to how vitamin C makes an essential contribution to the growth and repair of skin, it also helps with the wound healing process.
Firstly, the initial inflammatory response to a new wound requires ascorbic acid, and the vitamin also influences the production of scar tissue and new skin (4).
Furthermore, a vitamin C deficiency can have the severe effect of impairing wound healing in patients undergoing surgical procedures (5).
Key Point: Vitamin C helps to grow and repair our body's tissues, and an adequate level is important for wound healing.
2) Boosts Immune Response
Although there are claims that vitamin C supplements can help to prevent colds and illnesses, there is no evidence of this (6).
However, the nutrient does interact with the immune system, and studies show that it can upregulate immune response (7).
On this note, research demonstrates that a deficiency of vitamin C impairs immunity and puts people at higher risk for infections (8).
In short; mega-dosing vitamin C supplements will not help people avoid common colds.
Despite this, a diet that provides adequate amounts of vitamin C will help to keep the immune system strong and better fight any infections that do come along.
Key Point: Consuming sufficient amounts of vitamin C won't protect you from colds, but it will help to keep the immune system strong.
3) Improves Mood and Mental Health

There is evidence to suggest that sub-optimal vitamin C levels can increase the likelihood of depression and mood disorders (9).
On the positive side, research shows that increasing vitamin C intake has a positive impact on mood.
- In a randomized controlled trial, 205 elderly participants took 500 mg of vitamin C daily for 12 months. The results showed "significant changes" in mood and cognitive function, which both improved compared to placebo (10).
- Further randomized and controlled trials show that greater vitamin C intake can elevate mood and lower anxiety in high-school male students and young adult males (11, 12).
Key Point: Studies show that as vitamin C intake increases, overall mood improves.
4) Acts As An Antioxidant, Fights Oxidative Damage
Vitamin C consumption appears to be beneficial for the antioxidant properties it displays.
Antioxidants help to reduce the damage from inflammation and compounds like free radicals which can contribute to oxidative stress.
According to one study, vitamin C supplementation decreased the inflammation levels in athletes taking part in regular, intense exercise (13).
Furthermore, regular vitamin C intake significantly increases the concentration of plasma (in the blood) vitamin C (14).
One recent study also demonstrates that higher plasma vitamin C levels are inversely associated with all-cause mortality and the risk of stroke (15, 16).
Key Point: Vitamin C may have antioxidant effects in the body which could reduce inflammation.
5) Supports and Regenerates Vitamin E
One of the reasons we should emphasize whole foods over isolated vitamin supplements is because of the synergistic relationship some nutrients have.
For example, certain nutrients can have a beneficial impact on other nutrients, and this is the case with the relationship between vitamins C and E.
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin which also has antioxidant properties, and it helps to neutralize free radicals in the body (17).
However, when vitamin E neutralizes a free radical, it becomes oxidized itself.
On the positive side, vitamin C "recycles" oxidized vitamin E by donating an electron to it, and rescuing it from its oxidized state. Following this, vitamin E can resume its beneficial role in the body (18).
On the other hand; lower vitamin C levels mean higher levels of oxidized vitamin E.
Key Point: One of vitamin C's big benefits is the role it plays in "vitamin E recycling".
6) Prevents Scurvy From Developing
Insufficient dietary intake of vitamin C can lead to the development of scurvy.
Interestingly, scurvy may not be as much of an issue with very low carbohydrate diets because glucose and vitamin C appear to compete for cell uptake. If there is less glucose to contend with, then absorption of vitamin C will be higher (19).
Scurvy can lead to a range of complications, some of which can be severe.
In the past, sailors used to develop this condition on long journeys when they were limited to a regular diet of bread and alcohol.
Symptoms of scurvy may include weakness, joint pain, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, scurvy can be fatal (20).
Although it might not specifically be a health "benefit", preventing scurvy is a good reason to ensure sufficient intake of vitamin C.
Key Point: Adequate vitamin C levels prevent scurvy from developing.
7) Vitamin C Increases Calcium Absorption, Boosts Bone Health
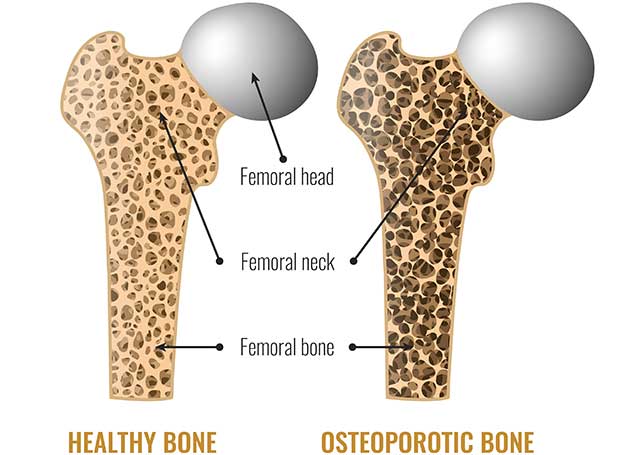
Going back to the synergy between different nutrients; there is a relationship between vitamin C and calcium.
Notably, vitamin C enhances the absorption of calcium in the intestines (21).
One of the benefits of this increased absorption is greater bone mass density, and therefore, improved skeletal health.
To explain; one study shows that postmenopausal women taking calcium alongside high vitamin C intake have increased bone mass density (22).
Further to this, a study among the Korean adult population found that the prevalence of osteoporosis drops as vitamin C intake increases (23).
Key Point: Vitamin C boosts absorption rates of calcium, and a greater intake may help to strengthen bone density.
8) Improves Skin Health
Vitamin C can improve skin health because it assists in the synthesis of collagen, which plays a crucial structural role in our skin (24).
Interestingly, research also demonstrates that there is an uptake of vitamin C into our skin, and higher levels can have several beneficial impacts.
According to recent research, these benefits include;
- Reducing the occurrence of wrinkles and lessening the wrinkle depth (25)
- Firmer looking skin, improved elasticity, and less "sagging" (26)
- Enhanced UV resistance and protection against sun damage (27)
As mentioned earlier, vitamin C also improves wound healing, which has a direct relationship with skin health.
Key Point: Higher levels of vitamin C have a range of benefits for skin health.
9) Helps To Mitigate the Damage From Smoking

As shown in the recommended daily allowance table for vitamin C, smokers have a higher requirement for this nutrient.
The reason why is simple; since smoking causes larger amounts of oxidative stress and inflammation, there is a greater need for the antioxidant effects of ascorbic acid.
Studies universally show that smokers have lower vitamin C statuses than non-smokers, suggesting that more of their vitamin stores are being used to "fight" the damage from smoking (28, 29).
The same thing occurs with vitamin E, another essential nutrient that smokers require in higher amounts.
Overall, the research suggests that it is probably wise for smokers to increase their vitamin C intake.
Key Point: Vitamin C requirements are higher for smokers.
10) Enhances the Absorption of Non-Heme Iron
There are two types of the mineral iron;
- Heme iron: we can find this form of iron in meat and animal products, and we can absorb around 14-18% of it.
- Non-heme iron: a form of the mineral found in plants which has a lower bioavailability of approximately 5-12% (30).
In other words; we can absorb the iron in animal foods much better than we can for plant-based sources of iron.
However, increasing the amount of vitamin C consumed alongside non-heme iron increases the absorption rate (31, 32).
Key Point: Consuming vitamin C with a source of non-heme iron has the favorable effect of increasing the rate at which we can absorb the iron.
11) May Help To Reduce the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease

There are claims based on epidemiology that higher vitamin C consumption can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular mortality (33, 34).
However, this has not been confirmed by any research to date.
Systematic reviews of the existing studies state that the evidence is low-quality and inconsistent (35, 36).
Vitamin C may have a positive impact on cardiovascular risk, but the existing evidence is not enough to state this with any certainty.
That said, there are mechanisms for how the vitamin may reduce cardiovascular risk.
For instance, short-term clinical trials and a systematic review of observational studies suggest that higher vitamin C intake reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure (37, 38).
Key Point: Vitamin C appears to help reduce blood pressure, and it may have cardiovascular benefits, but more high-quality research is necessary.
12) May Help With Macular Degeneration and Lower the Risk of Cataracts
Macular degeneration is the leading global cause of vision loss, and it affects millions of people around the world.
Although the condition cannot be cured, the existing evidence demonstrates that it is possible to slow the disease's progression.
According to the American Optometric Association, 500 mg or higher intake of vitamin C per day can slow progression (39).
Additionally, numerous studies show that a high intake of vitamin C may reduce the risk of developing cataracts (40, 41).
However, this data on cataracts is far from confirmed.
A recent systematic review of controlled studies found no evidence that vitamin C can prevent cataracts from forming (42).
Key Point: Vitamin C may help to slow the progression of macular degeneration. Data on cataracts is less clear.
13) May Benefit the Lipid (Cholesterol) Profile
A range of research studies demonstrates that vitamin C may have advantages for cardiovascular health, specifically for the lipid profile.
For instance, a meta-analysis of 13 randomized controlled clinical trials found that four weeks of vitamin C intake at 500 mg or higher leads to a "significant decrease" in LDL cholesterol and triglycerides (43).
Despite the effect on LDL and triglycerides, levels of HDL (the so-called "good cholesterol") stayed the same.
Regarding this, many researchers believe that the triglyceride to HDL ratio is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease (44).
Lowering triglycerides with HDL staying the same would improve this ratio.
Key Point: Consuming a prolonged high intake of vitamin C appears to improve the cholesterol profile.
Final Thoughts
This article shows that vitamin C can have several important health benefits.
That being said, it is important to note that some of these benefits are often exaggerated.
Neither vitamin C nor any nutrient in food is a miracle cure that will "prevent" or "cure" all kinds of conditions.
To sum up, an adequate level of vitamin C can help to promote good health as part of an overall healthy lifestyle.
For more information nutrients, see this guide to essential vitamins.
Source: https://www.nutritionadvance.com/vitamin-c-health-benefits/

Tidak ada komentar: